Aztec Labs -
Policy Principles
31 January 2024
INTRODUCTION
Aztec Labs is a software development company that builds open-source, credibly neutral, permissionless, blockchain-based solutions with a focus on zero-knowledge proof (“ZKP”) advancements.
We have a proven track record in developing ZKP solutions. Aztec Labs was the lead author of the seminal Plonk paper, which provided a more efficient, versatile, and user-friendly framework for ZKPs.
Currently, we are developing:
- an open-source programming language that allows for the safe, seamless construction of privacy-preserving ZKP cryptography circuits (“Noir”). Noir will enable an easier way for people without a PhD in cryptography to write encrypted smart contracts that utilize complex cryptographic primitives;
- a privacy-first Layer 2 on Ethereum (“Aztec”), enabling decentralized applications (“Apps”) to benefit from privacy and faster and cheaper transactions. Developers will write smart contracts on Aztec using Noir; and
- implementations of the following cryptographic schemes / protocols authored by Aztec Labs:
- Zeromorph: Zero-Knowledge Multilinear-Evaluation Proofs from Homomorphic Univariate Commitments; and
- Honk; a sum check-based zk-SNARK protocol with blazing-fast zk proof construction (paper yet to be published).
- Zeromorph: Zero-Knowledge Multilinear-Evaluation Proofs from Homomorphic Univariate Commitments; and
Our team of world-class cryptographers and engineers is developing Aztec to be launched as a credibly neutral and decentralized protocol, which will be operated and maintained by a distributed community of infrastructure providers and stakeholders.
As we redefine the possible with ZKPs, we are guided by certain core principles while navigating a rapidly evolving and uncertain global political/regulatory environment.
In 2023, we have proactively engaged with governmental authorities in the UK to help educate and shape crypto regulation:
- In February 2023, we responded to His Majesty’s Treasury (“HMT”) cryptoassets consultation, focusing on decentralized finance. Read our full response here. Many of our recommendations were taken on board by HMT in its response here.
- In June 2023, we responded to a joint Bank of England (“BoE”) and HMT consultation on the digital pound. Read our response here.
In 2024, we have proactively engaged with governmental authorities in the US to help educate and shape crypto regulation:
- In January 2024, we contributed to the DeFi Education Fund’s response to FinCEN re. its proposed rulemaking that would classify “Convertible Virtual Currency Mixing” as a class of transactions of primary money laundering concern. Read the response here.
In 2024 and beyond, we will continue to proactively engage with all stakeholders (including governmental authorities) to collaborate on future regulation and educate about the use cases of Aztec (see the Use Cases section below). Please get in touch with us at: hello@aztecprotocol.com should you wish to collaborate.
CORE POLICY PRINCIPLES
1) Privacy – privacy is a fundamental human right.
The right to privacy in the digital world, and access to privacy-preserving technologies, has become one of the most important human rights issues of the modern age. Not only in the web2 world but also in web3. Most existing blockchains (including Bitcoin and Ethereum) lack privacy. We want to change this and redefine the possible.
We are laser-focused on building and delivering the endgame for blockchain privacy. While many blockchain (including Layer 2) projects are focused on increasing scalability(1) and throughput, we believe the missing piece to enable the mass adoption of a blockchain-based internet reality is the development of credibly neutral programmable privacy.
We all expect privacy, in particular with personal information, payments, and our daily communications. As more existing internet applications move onto blockchain-based systems, users will expect the same (or higher) levels of privacy. We believe ZKPs can offer higher levels of privacy and usher in a new era of no-compromise privacy.
Privacy is the power to selectively reveal oneself to the world and Aztec will enable programmable privacy; the endgame. The ZKP-driven programmable privacy which will be enabled by Aztec has the potential to unlock a new era of innovation, financial inclusion, and economic growth in a similar way SSL encryption protocols transformed the internet by enabling e-commerce and social media.
Privacy is our guiding light and we will advocate for permissionless and credibly neutral privacy-enhancing technologies.
_________
(1) Note: many projects confusingly market privacy when they refer to ZKPs, but only use ZKPs for scalability.
2) Decentralization – decentralized systems empower the individual.
Centralized systems, which are in the hands of a few, enable the few to encroach on the freedoms of the many.
Decentralized systems protect this freedom.
Decentralization allows us to democratize systems by enabling credibly neutral internet infrastructure. Subsequently, users can trust the integrity of the entire system without relying on centralized authorities; promoting innovation, competition and ecosystem diversity; and allowing users more choice, more ownership (through self-custody of data which would also enable local computation without having to share any data) and most importantly, more freedom.
By way of example, there are fundamental differences between centralized systems and decentralized systems and between centralized finance (CeFi) and decentralized finance (DeFi). These differences justify different regulatory treatments. Different risks, different regulations.
Regulation should not seek to replicate traditional finance regulatory models – instead DeFi regulation should be highly bespoke and progressive and should take into account that:
- Users self-custody their data/value (and not via centralized intermediaries);
- DeFi solutions enable peer-to-peer transactions without taking the role of a traditional intermediary;
- DeFi models are not, therefore equivalent or comparable to CeFi or traditional intermediated financial services activities in terms of the risks that DeFi raises;
- Apps that facilitate access to or the use of DeFi protocols, and not the protocols themselves (nor the developers of such protocols), may be the appropriate hook for effectively regulating DeFi, noting that careful consideration of the characteristics of a particular App will be warranted when determining the kind of regulation (if any) that ought to apply to it; and
- decentralization plays a central role in DeFi, and developers need to be able to undertake a process of decentralization in relation to their protocols (including being able to issue/broadly distribute tokens) without being subject to burdensome regulatory requirements; and
- Imposing onerous and inappropriate (ctrl c + ctrl v CeFi regulations) regulatory requirements on decentralized system development teams risks undermining one of the key policy objectives financial regulation typically aims at: consumer protection.
Inappropriate regulation is likely to disincentive responsible and high-quality development of decentralized systems, as it: (i) may encourage development teams to seek to develop and deploy software on an anonymous basis, rather than operating as an identified project team with whom the public can interact in relation to the development of the protocol, reporting issues, fixing bugs, etc., (ii) may encourage development teams to conduct less testing or seek to offer less support for the protocol in the early stages following launch in order to avoid potentially being subject to onerous regulatory requirements, and (iii) finally, may encourage development teams to move out of a specific jurisdiction with such onerous laws. If regulation of decentralized systems is overly burdensome or unclear, the proliferation of decentralized system solutions is likely to be lower, forcing consumers to rely on a concentrated and interlinked group of CeFi intermediaries, and their attendant risks, to access crypto markets (it is interesting to consider, for example, the role DeFi could have played in mitigating concentration and consumer protection risks in the recent high profile failures of CeFi intermediaries such as FTX, if the regulatory environment in key global jurisdictions (such as the U.S.) had been more certain and proportionate).
Any effective regulatory regime for decentralized systems which seeks to support innovation and growth in the sector must therefore be tailored to take into account the progressive (and not immediate) process of decentralization, which is essential for the continued responsible development of decentralized systems.
Accordingly, Aztec Labs will:
- continue to engage with stakeholders and advocate for innovative and decentralization-focused solutions to address legal and regulatory challenges in decentralized systems;
- remain dedicated to educating policymakers about recognising progressive decentralization and safeguarding the integrity of decentralized systems and their users, protecting the freedom of self-ownership and self-custody.
3) Security – innovative safeguards and security practices are required to ensure decentralized systems are safe for users.
The security of users in decentralized systems is paramount.
This is particularly true when dealing with systems that incorporate new cutting-edge ZKP solutions that have not yet been battle-tested.
Decentralized systems and applications built on top of them need to be deployed prioritizing the security of users. User security is achieved through three main pillars:
- ensuring the system is credibly neutral, censorship-resistant, and immutable;
- transparency; both in respect of disclosures by developers and stakeholders as it relates to certain activities as well as open-source code, which can (and should) be audited; and
- a comprehensive strategy and innovative solutions that address safeguarding users from bugs, exploits, scams, and hacks, including potentially incentivising “white hats” (ethical security hackers) and balancing user safety of funds through immutability and the ability to quickly upgrade a system in case of unforeseen bugs.
At Aztec Labs, we are focused on contributing to the development of Aztec and Noir in accordance with these three pillars. We have a proven track record of encouraging transparent bug reporting and have paid out our largest bounty of US$450,000 in 2023 to a “white hat”.
We will continue to advocate for the above three pillars and ensure that regulation does not impede the development of safe and secure decentralized systems.
4) Open-Source – transparency in open-source development fosters innovation and enhances security
Open-source development fosters innovation and freedom; allowing contributors from around the world to build upon each other’s work, unlocking borderless collaboration leading to more creative solutions and safer and more secure systems.
Aztec and Noir are and will continue to be developed on an open-source basis.
We will advocate against any proposed laws or legislative initiatives that seek to regulate or punish open-source software developers for the writing and publishing of any code.
USE CASES
ZKPs have the ability to redefine how we think about managing and handling personal information by enabling users to protect and control their personal information or sensitive data (e.g., trade secrets) while meeting compliance requirements and verifying the authenticity of information.
Aztec is designed to offer developers (i) a unique “portal contract” architecture and (ii) the ability to implement “viewing keys” for users, which enables full control and flexibility to develop and deploy new use cases across an array of industries whether on-chain or off-chain, unlocking a new era of innovation. Below is a non-exhaustive overview of the broad use cases enabled by Aztec and Noir:
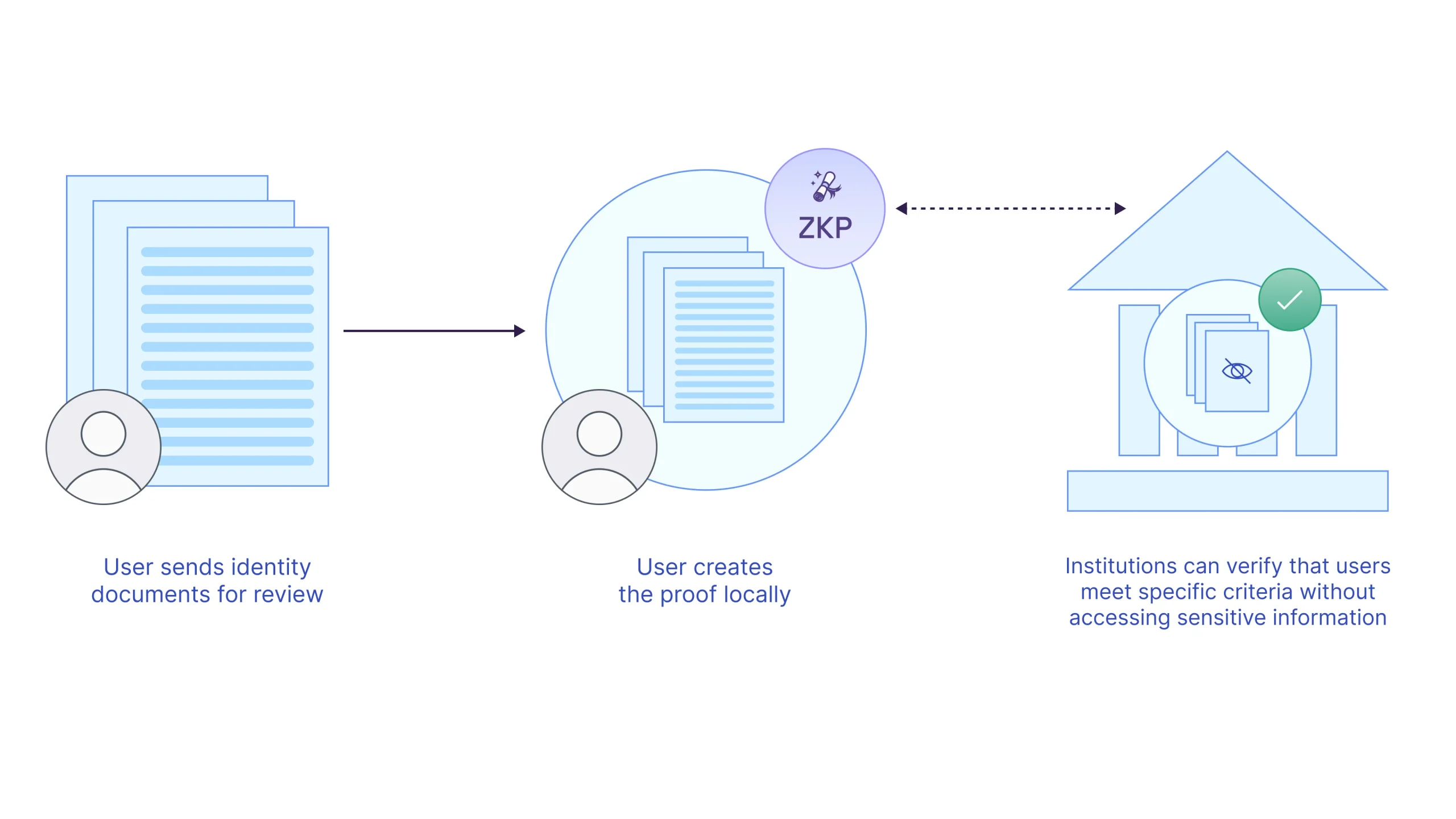
Privacy-Preserving Identity
Current identity management systems put personal information at risk of being breached or illegally accessed. ZKPs offer efficient tools to better manage and streamline the flow of information that needs to be collected from individuals. For example, Aztec can be used to develop decentralized identity management protocols allowing individuals to respond to identification requests (e.g., age, citizenship, or credit score) without revealing any sensitive personal information. Therefore, it reduces the risk of identity theft or unauthorized access to personal information. Similarly, it also relieves organizations from having to manage and secure users’ sensitive personal information, which can be costly and ultimately subject them to being the target of cyberattacks. At Aztec Labs, we have started to lay the building blocks of a privacy-preserving identity system and worked with the Verifiable Credentials Protocol to build smart contracts with Noir that verify users’ credentials while preserving their identities’ privacy.
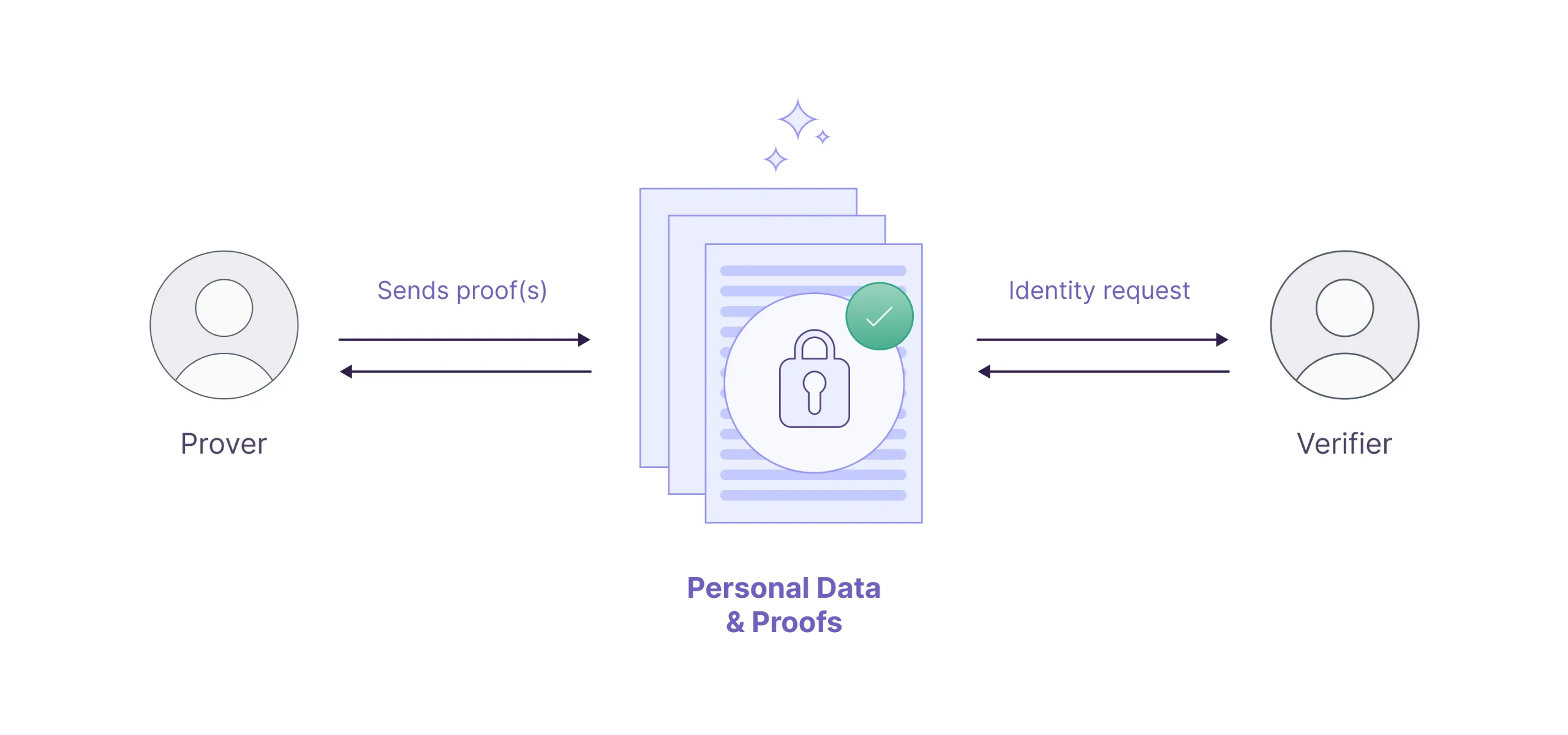
Implementing KYC Processes
Applicable legal requirements, such as know your customer (“KYC”) processes, often require banks and financial institutions to (i) confirm the identity of the organizations and individuals they do business with and ensure those entities act legally (e.g., ID card verification, face verification and documentation verification) or (ii) require additional documentation to be provided in order for an individual to complete a transaction. ZKPs offer the opportunity to streamline KYC processes without revealing sensitive personal information by verifying that someone meets specific criteria. With programmable private contracts, KYC is a part of the transaction logic, the transaction will only happen if the checks pass. For instance, Aztec Labs’ grantees have built zkPassport, which implements KYC processes to verify proof of passport (and requires different levels of information/verification depending on the amount of funds being transferred (much like the existing banking system, but all done virtually, in a non-custodial manner and therefore more secure)).
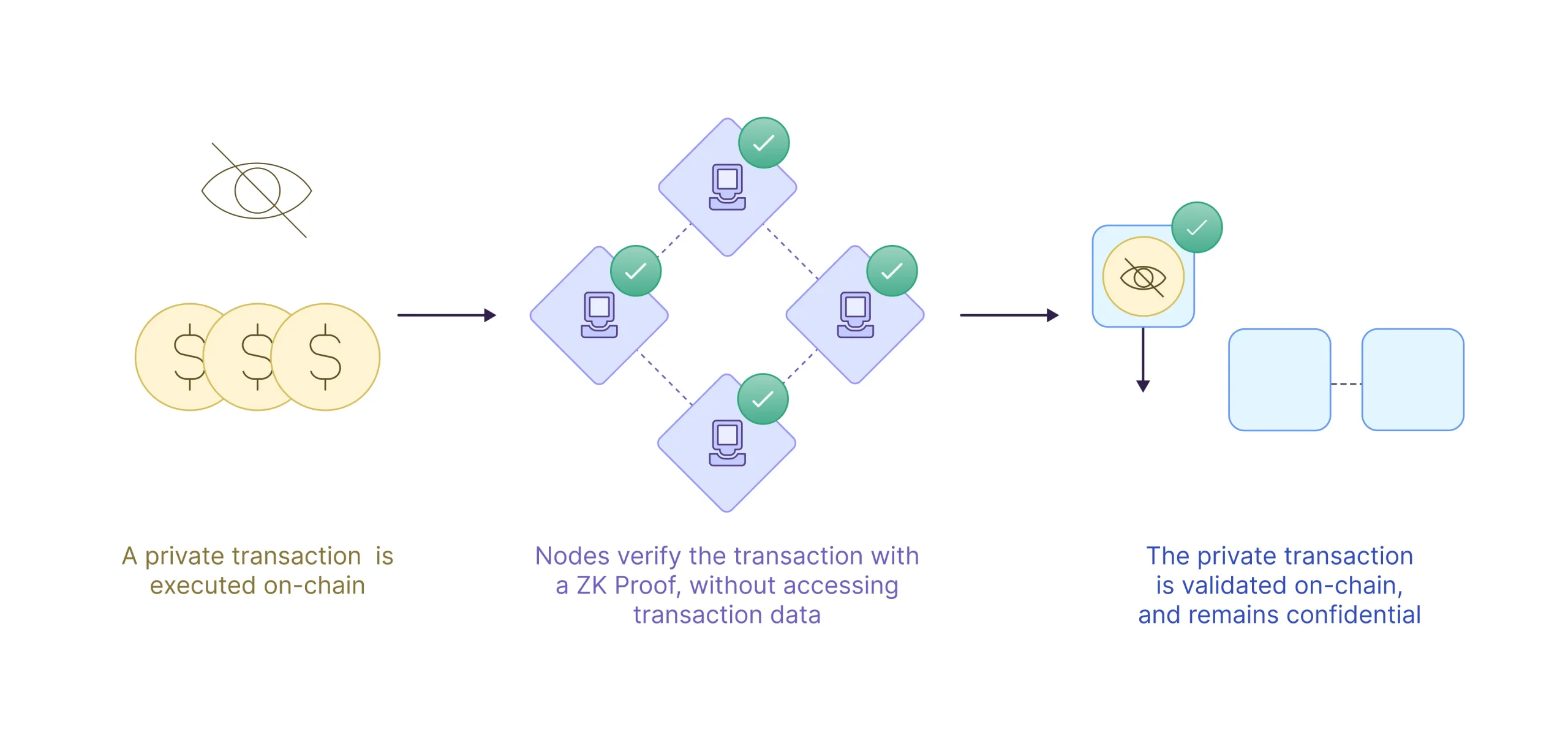
Securing Financial Transactions
Payments, whether on-chain or off-chain, are often visible to multiple parties, including payment providers and other interested parties. Revealing the identity of wallet holders and transaction details raises serious security threats for users. By baking in zero-knowledge technology, Aztec allows nodes to validate transactions without needing to access transaction data, per applicable laws and regulations. As a result, organizations building on Aztec can transact confidentially, on-chain, without revealing sensitive trade secrets, pricing data, and other sensitive information. Individuals will be able to further reduce the risk of being targeted by security attacks, unauthorized transactions, or identity theft. By enabling secure and private transactions that still meet regulatory requirements, Aztec tools can assist in bridging the gap between traditional finance and emerging financial technologies.
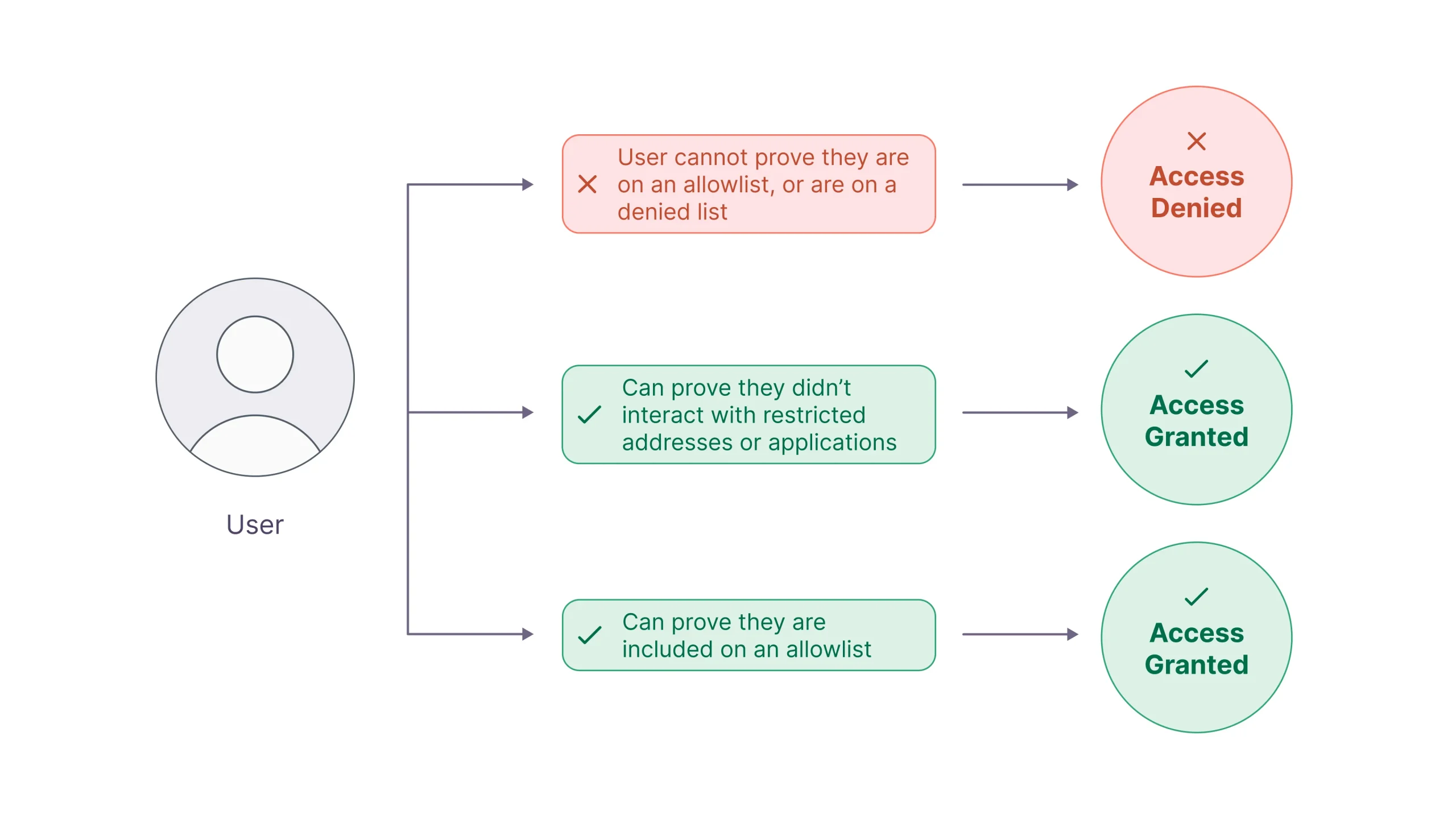
Access Control Implementations
ZKPs have the ability to restrict which users can or cannot access or interact with an application based on a set of predefined criteria (e.g., specific addresses, IP addresses, devices, user behavior, etc.). For example, users can generate valid proofs demonstrating that they are included on an allowlist based on predefined criteria. Conversely, they can prove they didn’t interact with restricted addresses or applications. This functionality can be used across any type of application.
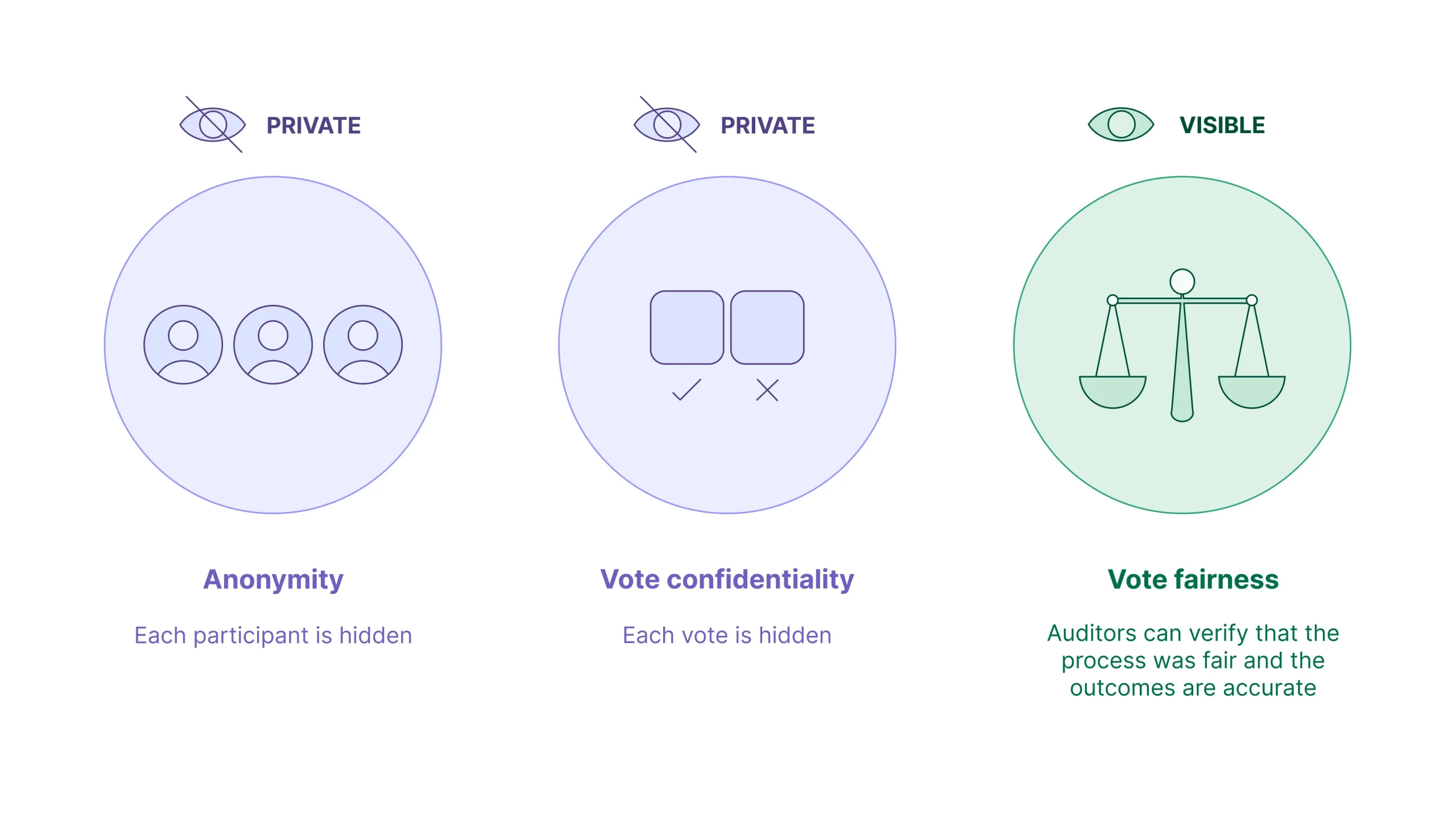
Reducing Voting Collusion
In traditional voting systems, individuals must confirm their identity in order to cast a ballot. Current on-chain democratic voting schemes are also public and transparent, allowing anyone to see who voted for which proposal. These systems raise risks of collusion or retaliation against their participants based on political beliefs. A ZKP-based voting protocol can be used to create highly secure and verifiable voting mechanisms that enable individuals to vote without revealing their identity or the nature of their vote. A ZKP verification would also enable independent auditors to verify that the process was conducted fairly and the election outcomes are accurate. At Aztec Labs, we have worked with Aragon and NounsDAO to develop a solution to enable private voting for NounsDAO. On Aztec, on-chain democratic voting with privacy can be a reality.
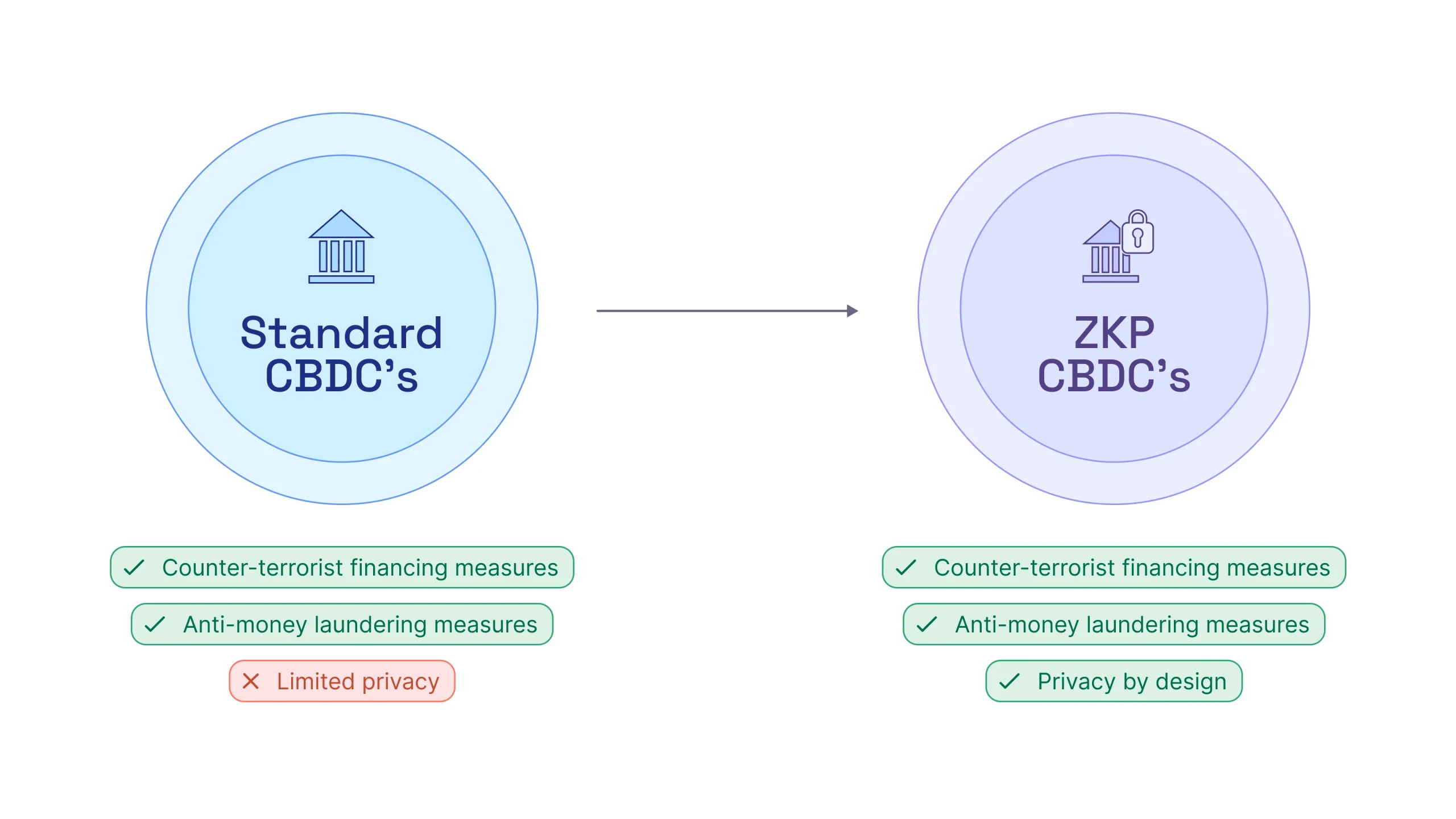
Privacy-Preserving CBDCs
ZKPs have the ability to address the privacy concerns surrounding Central Bank Digital Currencies (“CBDCs”) by facilitating the implementation of ‘privacy by design’ features without compromising the ability to deploy anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing measures. On 12 June 2023, Aztec Labs responded to the BoE and HMT consultation on the digital pound addressing how ZKPs can contribute to the development of privacy-preserving CBDCs. Read our response here.
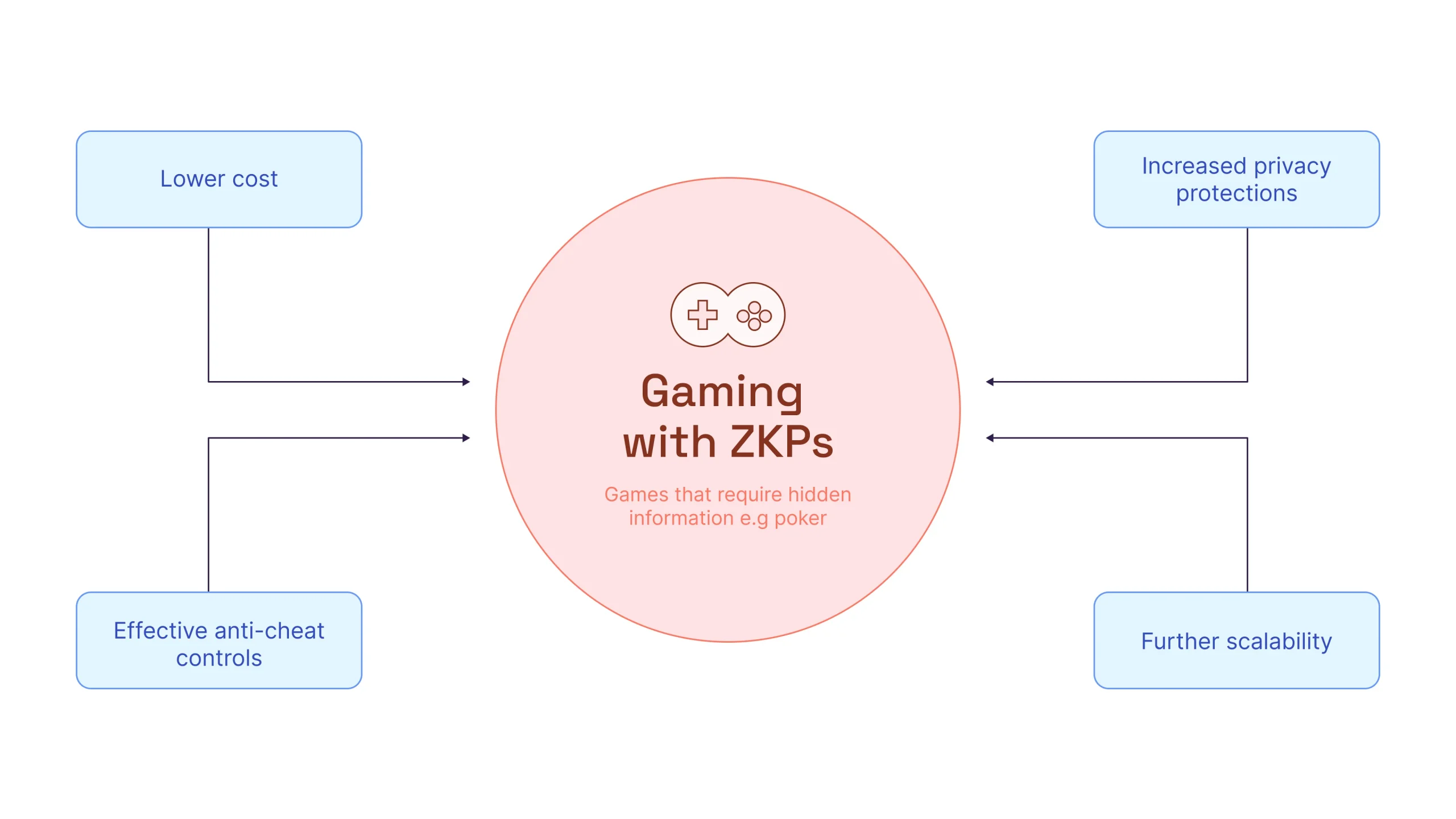
Gaming
The gaming industry has been transformed by the implementation of ZKPs through multiplayer gaming architecture and the way online games are hosted resulting in lower cost, increased privacy protections, effective anti-cheat controls and further scalability. Aztec Labs has been working with Dappicom to bring Nintendo games on-chain and allow users to prove in-game outcomes without revealing how.